By Ana Verayo, | April 12, 2016
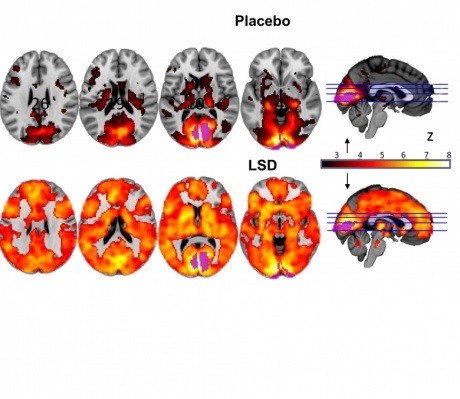
This image shows how, with eyes-closed, much more of the brain contributes to the visual experience under LSD than under placebo. The magnitude of this effect correlated with participants reports of complex, dreamlike visions.
Scientists discovered that a street drug known as acid for its hallucinogenic effects or LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide), apparently makes the human brain more "complete" according to a new study.
Like Us on Facebook
For the first time ever, brain scans show that just a dose of this psychedelic substance can affect overall brain activity and connectivity.These new brain scan images provided scientists the chance to analyze how visual hallucinations conjured up by an individual's brain along with his or her sense of "being one with the universe" upon taking an LSD trip.
According to co-author of the study, David Nutt of the Imperial College London who is also a neuropsychopharmacology professor, for the first time, we can see what is occurring inside the brain during a psychedelic state in order to better understand why LSD is having a profound impact on self awareness.
During their experiments, the team tested 20 healthy individuals where they were administered an injection of 75 micrograms of LSD in the first session, and a placebo on the next session. Scientists used three imaging methods namely the resting state of the brain on MRI, arterial spin labelling and magnetoencephalography in order to measure and create brain images of the participants during an LSD trip and while sober.
These brain scans observed and obtained from these participants show how they can experience several images that are emanating from many parts of the brain. Typically, these images are created by the brain's visual cortex which processes visual information.
Now, researchers say that during an LSD hallucination, these regions inside the brain that are otherwise separated, are now connecting with each other. These images also suggest that the brain regions that are normally grouped together also become segregated for those who are experiencing an LSD trip.
This apparent brain change also attributes to the individual's sense of "oneness with the cosmos" where experts also call this as "ego dissolution" which means that a typical sense of self will become broken down and replaced by one that connects them with others, their own selves and their natural, existing environment.
According to lead author of the study, Robin Carhart-Harris from the Imperial College of London, the human brain in an LSD state resembles the state of our brains when we are just infants, free and unconstrained, among many other ways. This can be linked to why infants are hyper emotional and have an imaginative nature of mind.
Harris explains that since humans develop into adulthood, the brain transforms into a more organized and compartmentalized one, where an individual's thinking becomes more mature and rigid. Details about this new study are published on the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
-
Use of Coronavirus Pandemic Drones Raises Privacy Concerns: Drones Spread Fear, Local Officials Say

-
Coronavirus Hampers The Delivery Of Lockheed Martin F-35 Stealth Fighters For 2020

-
Instagram Speeds Up Plans to Add Account Memorialization Feature Due to COVID-19 Deaths

-
NASA: Perseverance Plans to Bring 'Mars Rock' to Earth in 2031

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
COVID-19: Doctors, Nurses Use Virtual Reality to Learn New Skills in Treating Coronavirus Patients